Friday, January 1, 2010
Sunday, August 9, 2009
The Periodic table
• The lements are arranged in periods and groups.
Period:
• A period is a horizontal raw of elements.
• There are seven periods.
• The period number refers to the number of shells present in an element.
For example: The element carbon and sodium.
Carbon has two shells, therefore it belongs to period two. Like wise sodium has three shells so it belongs to period three.
• First period consists of two elements. They are hydrogen and Helium.
• The second and the third period consists of eight elements.
• The fourth and the fifth period consists of eighteen elements.
Friday, June 5, 2009
Giant Molecular structure
E.g.: - Diamond, graphite, silicon (IV) oxide (silica)
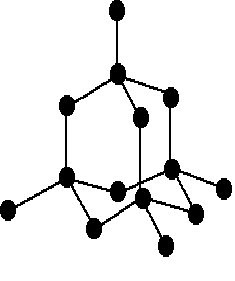
• Each single crystal if a diamond is one giant molecule. carbon atom is bonded to other carbon atoms tetrahedrally.
• All the four outermost electrons in carbon atom are involved in the bond formation and there are no free electrons to move. therefore diamond does not conduct electricity.
• A lot if energy is required to break apart the strong covalent bonds between the carbon atoms, hence diamond has very high melting & boiling point.
• Diamond is the hardest substance known since the carbon atoms are not able to slide over each other due to strong covalent bonds.
• Diamond is a transparent, colourless crystal.
Structure of Graphite
• Graphite has a layered structure each carbon is bonded to three other carbon atoms in a hexagonal arrangement to form rings of regular hexagons. the different layers are held together by weak vanderwaal's force of attraction.
• Graphite has very high melting & boiling point. therefore a lot of energy is required to break apart the strong covalent bonds between the carbon atoms.
• It is a good conductor of electricity because each carbon atom uses only 3 out of 4 outer electrons for bonding with one free electron to conduct electricity.
• The weak vanderwaal's force between the layers enables layers to slide over each other. hence graphite is a soft substance.
• It is black, opaque and shiny solid.

Structure of Polythene
• Polythene is a plymer. It is made up of thousands of molecules called monomers joined together in long chains. The monomer used in making polythene is called ethene.
• Polythene has high melting point and does not conduct electricity.
• Polythene can be softened on heating and melting and set again when cooled.
Monday, June 1, 2009
Simple Molecular structure
• A simple molecular structure contains small molecules.
• Simple molecular structure are formed from only a few atoms.
• They have strong covalent bonds between the atoms with in a molecule, what have weak bonds between molecules is called as Vanderwaal’s force.
• These vanderwaal’s forces increase steadily with the increasing size of the molecules.
• Most of the simple molecular structures are liquids or gases under normal conditions.
• In simple molecular structures the forces between the molecules in the solid and liquid state are weak such that very little energy is needed to break up the structure.
E.g.: - Methane (CH4), Iodine (I2), Water (H2O), Carbon dioxide (CO2)
Structure of Methane
This is the tetrahedral shake of methane molecule. The carbon-hydrogen bond is a strong covalent bond. There is weak vanderwaal’s force is between the molecules of methane.
Structure of Iodine
Iodine has a crystal structure in which iodine molecules are packed together. The force between the molecules are weak so iodine is a flaky solid that sublimes if heated gently iodine crystals can be crushed easily.
Elements, Compounds & Mixtures
• An element is made up of only one types of atom.
• Elements are substances that cannot be broken down chemically into smaller substances.
E.g.: - Carbon, Nitrogen, Oxygen, Calcium, Helium etc.
Compounds:
• A compound is made up of two or more different kinds of atoms chemically combined together.
E.g.: - Water, Hydrochloric acid, Carbon monoxide etc.
Mixtures:
Mixtures are the substances that are simply mixed together without any chemical reaction taking place between them. A mixture is made up of two or more elements or compounds physically combined together. The individual substances can be separated by physical means.
E.g.: - Air, Sea water etc.
Tuesday, May 26, 2009
Electronic configuration of Ions
• Ions with single positive charge are formed when an atom loose one electron.
E.g.: - Sodium atom (Na) loose one electron to form sodium ion (Na+)
E.g.: - Beryllium atoms (Be) loose 2 electrons to form beryllium ion (Be²).
• Negative ions are formed when atoms gain electrons.
• Ions with single negative charge are formed when an atom gains one electrons
E.g.: - Chlorine (Cl) atom gains one electron to form chloride ion (Cl−).
E.g.: - Oxygen (O) atom gain 2 electrons to form oxide ion (O²−).
•
Friday, May 22, 2009
Electron Arrangement in Atoms
• This arrangement of electrons around the nucleus of an atom is called electronic configuration.
• Shells are numbered starting from the shell which is nearest to the nucleus of the atom.
• Hence the shell which is furthest away from nucleus is called the outermost shell and the electrons in the shell are referred to as the outermost electrons.
• The shell nearest to nucleus is called the first shell and this is also the lowest energy level.
• Each shell can hold a fixed number of electrons. The formula helps us to find the number of electrons in each shell. And the formula is 2n² where ‘n’ is the shell number.
For the first 20 elements (hydrogen to calcium)
» The first shell (lowest energy level) can hold maximum of 2 electrons.
» The second shell can hold a maximum of 8 electrons.
» The third shell can hold a maximum of 8 electrons.
» The remaining electrons are placed in the fourth shell.
» The energy levels must be filled in order of increasing energy. The first level is filled first before going to the second level and subsequent higher levels.