E.g.: - Diamond, graphite, silicon (IV) oxide (silica)
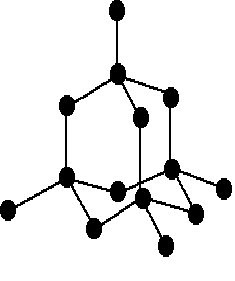
• Each single crystal if a diamond is one giant molecule. carbon atom is bonded to other carbon atoms tetrahedrally.
• All the four outermost electrons in carbon atom are involved in the bond formation and there are no free electrons to move. therefore diamond does not conduct electricity.
• A lot if energy is required to break apart the strong covalent bonds between the carbon atoms, hence diamond has very high melting & boiling point.
• Diamond is the hardest substance known since the carbon atoms are not able to slide over each other due to strong covalent bonds.
• Diamond is a transparent, colourless crystal.
Structure of Graphite
• Graphite has a layered structure each carbon is bonded to three other carbon atoms in a hexagonal arrangement to form rings of regular hexagons. the different layers are held together by weak vanderwaal's force of attraction.
• Graphite has very high melting & boiling point. therefore a lot of energy is required to break apart the strong covalent bonds between the carbon atoms.
• It is a good conductor of electricity because each carbon atom uses only 3 out of 4 outer electrons for bonding with one free electron to conduct electricity.
• The weak vanderwaal's force between the layers enables layers to slide over each other. hence graphite is a soft substance.
• It is black, opaque and shiny solid.

Structure of Polythene
• Polythene is a plymer. It is made up of thousands of molecules called monomers joined together in long chains. The monomer used in making polythene is called ethene.
• Polythene has high melting point and does not conduct electricity.
• Polythene can be softened on heating and melting and set again when cooled.